AI in Vulnerability Trends Analysis
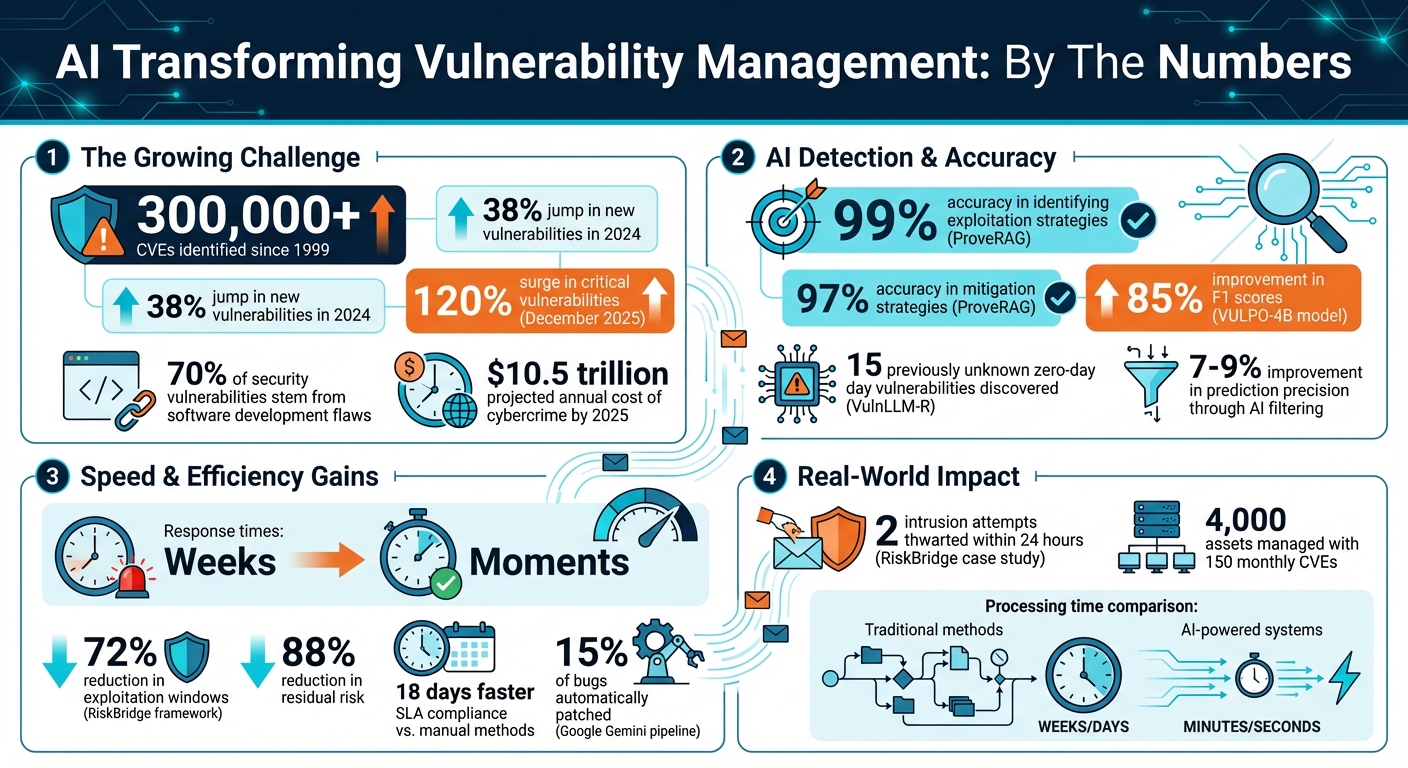
AI is transforming how we handle cybersecurity threats by automating the detection, prediction, and prioritization of vulnerabilities. With over 300,000 CVEs identified since 1999 – and a 38% jump in new vulnerabilities in 2024 alone – manual methods are no longer practical. AI tools now analyze massive datasets, predict zero-day exploits, and help security teams act faster.
Key Takeaways:
- AI Speeds Up Detection: AI systems identify zero-days and cut response times from weeks to moments.
- Improved Accuracy: Tools like ProveRAG achieve 99% accuracy in identifying exploitation strategies.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI predicts threats by analyzing behavior patterns and prioritizes vulnerabilities based on real-world risks.
- Automation in Action: In 2025, AI frameworks like RiskBridge reduced exploitation windows by 72% for businesses.
AI is not just about finding vulnerabilities – it’s helping fix them. With tools like Google’s Gemini pipeline automating code fixes, the future may bring self-healing systems. However, trust remains a challenge, pushing for Explainable AI (XAI) to ensure transparency in decision-making.
AI is shaping cybersecurity into a faster, smarter, and more proactive field, helping organizations stay ahead in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
AI Impact on Vulnerability Management: Key Statistics and Performance Metrics
Key Applications of AI in Vulnerability Trend Analysis
AI for Identifying Emerging Vulnerability Trends
AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to sift through vast amounts of unstructured data – like CVE reports, developer comments, dark web discussions, and open-source intelligence – and quickly identify patterns. Machine learning models take this data and uncover common threads between different attacks, helping to detect broader threat trends before they gain traction.
For example, in December 2025, Recorded Future‘s Enterprise AI for Intelligence analyzed the CVE landscape for that month and uncovered a 120% surge in critical vulnerabilities. Among these, the system flagged "React2Shell" (CVE-2025-55182) as the most pressing threat within Meta’s React framework. This early identification allowed security teams to focus their resources on mitigating the most dangerous risks.
These findings lay the groundwork for predictive models that take risk detection to the next level.
Predictive Analytics for Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
AI doesn’t just identify trends – it also predicts zero-day threats by analyzing deviations in behavior. Unlike traditional systems that rely on signatures to recognize known threats, AI-powered predictive models use unsupervised learning to spot anomalies in network traffic and system logs. By examining historical data and behavioral patterns, these models estimate the likelihood and urgency of potential exploits.
Take POLAR, an advanced framework that moves beyond static severity scores. It evaluates temporal factors like the time between vulnerability disclosure and proof-of-concept exploitation, discussions on the dark web, and vendor advisories. This allows it to calculate the probability of exploitation within 30 days. With this data, security teams gain a clearer picture of not just what is vulnerable but how quickly they need to act.
Automated Vulnerability Prioritization
AI also revolutionizes how vulnerabilities are prioritized. Instead of relying solely on static CVSS scores, AI introduces dynamic risk models that consider both real-world exploitability and an organization’s specific business context. By combining data from vulnerability scanners, asset inventories, and live threat feeds, machine learning algorithms identify which vulnerabilities pose the most immediate and serious risks.
In June 2025, a small-to-medium enterprise managing 4,000 assets used the RiskBridge AI framework to handle 150 new monthly CVEs. While traditional CVSS rankings flagged a Windows TCP/IP vulnerability (CVE-2024-38063) as the top priority, RiskBridge identified a backdoor in xz-utils (CVE-2024-3094) as the real threat. This was due to active exploitation attempts and its impact on the company’s production CI/CD pipelines. Acting on this insight, the enterprise cut the exploitation window by 72% and thwarted two intrusion attempts within 24 hours. The framework also achieved an 88% reduction in residual risk and sped up SLA compliance by 18 days compared to manual methods.
AI-driven prioritization doesn’t just improve accuracy – it also reduces alert fatigue. Automated systems can apply patches or isolate high-risk vulnerabilities immediately, while routing lower-priority issues to ticketing systems for manual follow-up.
sbb-itb-9b7603c
Recent Research and Studies in AI-Driven Vulnerability Analysis
CVE Growth and AI’s Role in Analysis
As the cybersecurity landscape grows more complex, the need for faster, scalable detection methods has become undeniable. Consider this: 70% of security vulnerabilities stem from flaws in the software development process, and the financial toll of cybercrime is projected to soar to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. With such staggering figures, traditional tools simply can’t keep up with the sheer volume of data.
This is where AI-powered tools step in. A systematic review spanning 29 studies from 2019 to 2024 revealed that AI significantly outperforms traditional rule-based methods, offering better precision, scalability, and speed in detecting vulnerabilities. For instance, modern retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems now cross-reference real-time National Vulnerability Database (NVD) data to stay on top of emerging threats.
One notable example is ProveRAG, introduced in February 2025 by researchers Reza Fayyazi, Stella Hoyos Trueba, Michael Zuzak, and Shanchieh Jay Yang. This system leverages automated retrieval-augmented large language models (LLMs) to analyze Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) by cross-referencing NVD and Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) data. ProveRAG achieved over 99% accuracy in identifying exploitation strategies and 97% accuracy in mitigation strategies. The research team emphasized the importance of these advancements:
The sheer volume of known vulnerabilities complicates the detection of patterns for unknown threats… accuracy and up-to-date information are paramount.
These breakthroughs highlight how AI is reshaping vulnerability analysis, paving the way for real-world applications in automated remediation.
Case Studies of AI-Powered Vulnerability Tools
Recent case studies showcase how AI is evolving beyond detection to tackle automated remediation. For example, Google Security Engineering developed a Gemini-powered pipeline capable of generating code fixes for sanitizer bugs in C/C++, Java, and Go. This system patched 15% of bugs identified during unit tests, producing hundreds of fixes and significantly cutting down manual effort. As Jan Keller and Jan Nowakowski from Google Security Engineering noted:
Every bug uncovered is an opportunity to patch and strengthen code – but as detection continues to improve, we need to be prepared with new automated solutions that bolster our ability to fix those bugs.
Another standout is the VULPO-4B model, which, in November 2025, achieved an 85% improvement in F1 scores compared to baseline models, performing on par with DeepSeek-R1-0528 – a model 150 times its size. Similarly, in December 2025, the VulnLLM-R reasoning model, a specialized 7-billion parameter system, uncovered 15 previously unknown zero-day vulnerabilities when tested on popular repositories like Assimp, SQLite3, and CUPS.
AI is even enhancing the quality of vulnerability datasets. By using LLMs to filter out inaccuracies in vulnerability patch data, prediction precision for automated models improved by 7% to 9%. This demonstrates how AI can refine not just detection but the entire research and remediation process.
How The Security Bulldog Improves Vulnerability Management
AI-Powered NLP for Open-Source Intelligence
The Security Bulldog uses its advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) engine to sift through vast amounts of unstructured Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) data. This includes sources like threat reports, GitHub commits, vendor advisories, social media updates, and news articles. By doing so, it extracts key indicators from this sea of information to help identify potential threats more effectively.
With the help of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), the platform fills in the gaps found in incomplete or vague CVE descriptions by pulling in additional context from public data sources. This enriched context covers every stage of threat management – from attribution and analysis to remediation – ensuring cybersecurity teams get actionable insights rather than overwhelming data dumps. These detailed insights make prioritizing vulnerabilities much quicker and more precise.
Faster Vulnerability Prioritization
The platform simplifies decision-making by automatically ranking vulnerabilities based on risk factors specific to your IT setup. It evaluates elements like threat severity, exploitability, and how relevant the vulnerability is to your infrastructure. This automation saves teams a significant amount of time.
By pulling live data from trusted sources like the NVD, EPSS, and CISA KEV via REST APIs, The Security Bulldog provides real-time intelligence. This ensures teams focus on the vulnerabilities that matter most, avoiding the trap of treating every alert as equally urgent.
Integration with Existing Cybersecurity Workflows
Once vulnerabilities are prioritized, The Security Bulldog takes it a step further by streamlining remediation processes. It connects and centralizes intelligence from various security tools, such as vulnerability scanners, ITSM platforms, and patch management systems. Additionally, it integrates seamlessly with SOAR and SIEM solutions to speed up detection-to-resolution workflows.
The platform allows teams to import and export internal data while maintaining their current processes. It supports frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, CVE databases, and even custom feeds tailored to specific IT environments. This flexibility ensures better collaboration without disrupting established workflows.
For businesses, the Enterprise plan accommodates up to 10 users at $850 per month, while the Enterprise Pro plan offers custom SOAR/SIEM integrations and training for larger teams. By consolidating data and automating workflows, The Security Bulldog showcases how AI can transform the way vulnerabilities are managed.
AI Agents for Cybersecurity: Enhancing Automation & Threat Detection
The Future of AI in Vulnerability Trends Analysis
As AI continues to redefine vulnerability management, the next frontier lies in automating remediation. While tools like The Security Bulldog already streamline vulnerability detection and prioritization with real-time insights, the future promises systems capable of not only identifying threats but also fixing them without human input.
Google’s early experiments suggest a world where AI could autonomously repair vulnerabilities, paving the way for self-healing systems. This marks a transformative shift: AI evolving from a diagnostic tool to an active problem-solver.
"As detection continues to improve, we need to be prepared with new automated solutions that bolster our ability to fix those bugs." – Jan Keller and Jan Nowakowski, Google Security Engineering
Recent high-profile deployments have shown that AI can already uncover and address vulnerabilities without human intervention. These advancements highlight the rapid movement toward automated remediation, but they also reveal a significant challenge: trust.
The Trust Challenge: Explainable AI (XAI)
One of the biggest hurdles to fully embracing AI in cybersecurity is the "black-box" nature of many models. Security teams are understandably cautious about allowing opaque systems to make critical decisions, especially for essential infrastructure. This is where Explainable AI (XAI) becomes crucial. By making AI’s decision-making processes transparent, XAI can help bridge the trust gap between machines and humans.
As Malek Malkawi from Istanbul Medipol University explains:
"The black-box nature of most models poses a serious problem in terms of trust. Thus, XAI is quite pertinent in this context".
Incorporating XAI into future AI systems will be essential as these technologies take on more responsibility within critical workflows.
The AI Arms Race in Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity field is rapidly becoming an AI battleground. With the global cost of cybercrime expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, both attackers and defenders are racing to leverage AI. The challenge isn’t just about developing better tools; it’s about speed. Traditional security research struggles to keep pace with the rapid evolution of software and AI technologies.
To stay ahead, organizations will need platforms that combine advanced natural language processing (NLP) with real-time intelligence feeds. These systems will be key to tracking and neutralizing threats that evolve faster than human analysts can manage. The future of cybersecurity will belong to those who can adapt to this accelerating landscape.
FAQs
How does AI enhance vulnerability detection speed and accuracy?
AI has transformed vulnerability detection by automating intricate tasks. With tools like large language models (LLMs) and transformer-based systems, it can swiftly process vast amounts of code and vulnerability data with impressive accuracy. This reduces false positives, freeing up cybersecurity teams to concentrate on genuine threats.
By simplifying the detection process, AI accelerates triage and remediation efforts, giving teams more time to address pressing concerns. It also uncovers trends in potential risks, helping organizations tackle vulnerabilities early – before they develop into major problems.
How does Explainable AI (XAI) improve cybersecurity?
Explainable AI (XAI) is transforming cybersecurity by bringing clarity to how AI-driven systems operate. As these systems grow more capable of identifying vulnerabilities and analyzing threats, XAI ensures that their decision-making processes are transparent and understandable. This transparency helps security teams build trust in the system’s insights, verify findings, and take precise, well-informed actions.
When AI highlights vulnerabilities or flags potential threats, XAI steps in to provide detailed explanations. This added layer of clarity enables teams to respond more quickly and efficiently. In high-stakes scenarios – where a missed threat or a false alarm could have serious consequences – this interpretability becomes indispensable. By making AI tools easier to understand and trust, XAI empowers organizations to bolster their security efforts and make smarter, more confident decisions.
How does AI help predict zero-day vulnerabilities before they are exploited?
AI plays a crucial role in predicting zero-day vulnerabilities by leveraging machine learning and deep neural networks to study software behavior and uncover unusual patterns in code. These systems excel at spotting anomalies that could signal security weaknesses, often identifying potential flaws before attackers have a chance to exploit them.
On top of that, advanced AI tools use methods like fuzzing and large language models (LLMs) to streamline the process of vulnerability detection. By examining attacker behaviors and analyzing emerging threat signals, AI delivers early warnings, allowing security teams to act quickly and mitigate risks. This proactive approach helps organizations strengthen their defenses against zero-day threats and enhances their overall cybersecurity posture.