How to Prioritize Patches with AI Scoring
Every day, security teams face a flood of vulnerabilities, but only a fraction can be patched. Traditional methods, like CVSS scores, often label too many vulnerabilities as critical, overwhelming teams and leaving real threats unaddressed. AI scoring changes this by focusing on what matters most: the likelihood of exploitation and its impact on your systems.
Here’s why AI scoring works:
- Dynamic Updates: AI uses real-time data, unlike static CVSS scores, to adjust risk levels based on new threats.
- Smarter Prioritization: It narrows down critical vulnerabilities from 60% to just 1.6%, saving time and effort.
- Data-Driven Decisions: AI integrates threat intelligence, exploit availability, and asset importance to predict risks.
Organizations using AI scoring have reduced patching workloads by 90%, cut downtime by 86%, and saved over 15 hours per week. The key is integrating AI into your workflow, connecting it to scanners, threat feeds, and patch management systems for automated, precise results.
AI SECURITY MASTERCLASS: Avoid Vulnerability Overload, Focus on Clear Risk Priorities
How AI Risk Scoring Improves on CVSS
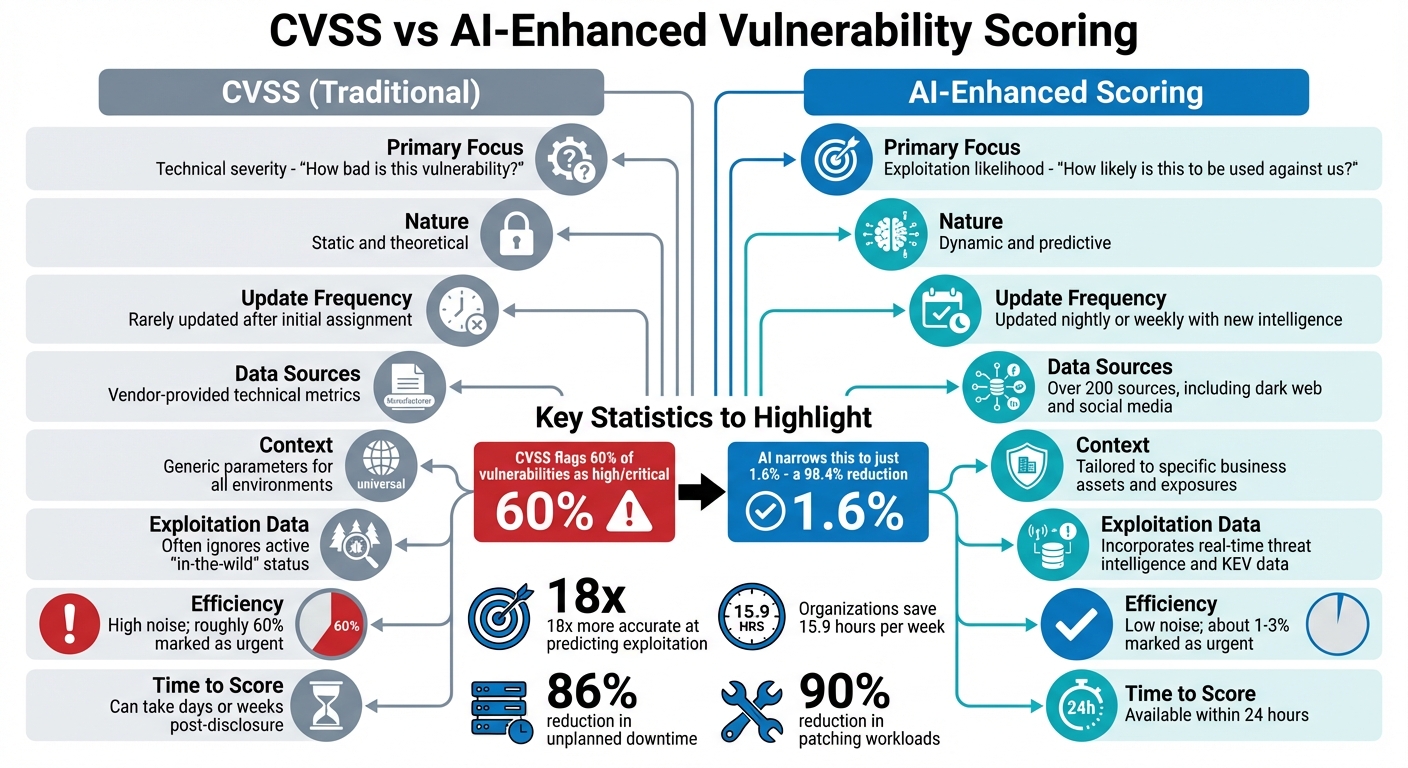
CVSS vs AI-Enhanced Vulnerability Scoring Comparison
For years, CVSS has been the go-to system for assessing the severity of vulnerabilities. However, it’s not designed to predict whether a vulnerability will actually be exploited. As Jorge Orchilles from SCYTHE explains:
"CVSS is a scoring system, not a risk rating system".
CVSS focuses on the theoretical damage a vulnerability could cause, without considering whether attackers are actively exploiting it or if it affects critical systems.
AI-driven risk scoring takes a different approach, prioritizing the likelihood of real-world exploitation over hypothetical risks. While CVSS classifies about 60% of vulnerabilities as "high" or "critical", AI models narrow that down to just 1.6% – a staggering 98.4% reduction in the number of vulnerabilities demanding immediate attention. This allows security teams to focus on the threats that truly matter, avoiding wasted effort on low-risk issues.
AI scoring is also 18 times more accurate than CVSS at predicting exploitation, saving teams an average of 15.9 hours per week and reducing unplanned downtime by 86%. This shift represents a move from reactive responses to a more proactive and strategic defense. These limitations in CVSS have driven the adoption of AI-driven models, which address these gaps in a smarter way.
Key Factors in AI‑Driven Risk Scoring
AI scoring builds on its ability to filter out noise and identify critical threats by evaluating vulnerabilities on multiple dimensions that CVSS overlooks. For example, it assesses exploit maturity – whether the exploit is purely theoretical, has been tested in labs, or is actively being used in widespread attacks. It also monitors sources like the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog and ExploitDB to determine if a flaw is being actively weaponized.
Another key factor is asset criticality. AI models evaluate whether a system is internet-facing, isolated, handles sensitive data, or is part of critical infrastructure. Using graph-based analysis, these models can even identify vulnerabilities that could enable lateral movement or privilege escalation within a network.
Threat intelligence integration is a cornerstone of AI scoring. These systems pull data from a wide range of sources, including social media, dark web forums, and news feeds, to detect early indicators of potential threats. Some models, like Vulners AI v2, retrain weekly using algorithms like CatBoost to stay ahead of new exploit techniques and attacker strategies. This means scores can be available within 24 hours of a vulnerability’s disclosure – often faster than the National Vulnerability Database can publish a CVSS rating.
In October 2024, researchers Corren McCoy, Ross Gore, Michael L. Nelson, and Michele C. Weigle applied an AI ranking model to software inventories at multiple universities. By combining data from sources like MITRE ATT&CK, CAPEC, and the NVD, the model identified vulnerabilities specifically targeted by threat actors in the education sector. The study improved the identification of high-risk vulnerabilities by 71.5%–91.3% and projected annual patching cost savings of 23.3%–25.5%.
These advanced assessments are making it easier to integrate AI scoring into patch management workflows.
CVSS vs AI‑Enhanced Scoring
The table below highlights the key differences between CVSS and AI-enhanced scoring:
| Feature | CVSS (Traditional) | AI‑Enhanced Scoring |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Technical severity: "How bad is this vulnerability?" | Exploitation likelihood: "How likely is this to be used against us?" |
| Nature | Static and theoretical | Dynamic and predictive |
| Update Frequency | Rarely updated after initial assignment | Updated nightly or weekly with new intelligence |
| Data Sources | Vendor-provided technical metrics | Over 200 sources, including dark web and social media |
| Context | Generic parameters for all environments | Tailored to specific business assets and exposures |
| Exploitation Data | Often ignores active "in-the-wild" status | Incorporates real-time threat intelligence and KEV data |
| Efficiency | High noise; roughly 60% marked as urgent | Low noise; about 1–3% marked as urgent |
| Time to Score | Can take days or weeks post-disclosure | Available within 24 hours |
Ray Carney, Research Director at Tenable, sums it up well:
"CVSS is not an efficient predictor of exploitation, which isn’t surprising given that CVSS was not built to be [one]".
While CVSS provides valuable technical insights, relying on it alone can overwhelm teams with alerts, making it harder to focus on the vulnerabilities that truly matter. AI-driven scoring complements CVSS by delivering the predictive insights needed to stay ahead of attackers.
Adding AI Scoring to Your Threat Intelligence Workflow
Integrating AI scoring into your vulnerability management process doesn’t mean starting from scratch. The trick lies in linking your existing tools to AI-powered platforms capable of automatically ingesting, analyzing, and prioritizing threats based on actual risk rather than static severity ratings.
Start by evaluating your current scan schedules, patching routines, and remediation strategies. Once you have a clear picture, connect AI scoring systems with external threat intelligence feeds and automate the prioritization process. This approach can significantly reduce manual effort – by as much as 80% – saving around 15.9 hours per week and cutting unplanned downtime by 86%. This shift moves your team from constantly reacting to proactively defending against threats.
From there, the next step is to bring together diverse threat intelligence sources into your workflow.
Connecting Threat Intelligence Feeds
AI scoring platforms excel at pulling data from hundreds of sources simultaneously – something that would be impossible for any human team to manage manually. These systems can process both structured data (like CVE databases, MITRE ATT&CK frameworks, and CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog) and unstructured data (such as dark web forums, social media, news articles, and security podcasts).
Natural Language Processing (NLP) engines handle the heavy lifting by analyzing millions of unstructured documents daily to uncover new threats. For example, platforms like The Security Bulldog rely on proprietary NLP engines to distill actionable insights from sources like MITRE ATT&CK, CVE databases, and news feeds. Future plans include integrating data from Twitter/X and dark web monitoring, ensuring your team gains valuable intelligence without hours of manual research.
This approach creates a unified view of risks. In October 2024, researchers Corren McCoy, Ross Gore, Michael L. Nelson, and Michele C. Weigle demonstrated how connecting data from CVE, MITRE ATT&CK, and ExploitDB into a knowledge graph improved the identification of exploited vulnerabilities by 71.5%–91.3% and reduced annualized patching costs by 23.3%–25.5% across six universities and four government facilities.
To streamline this process, connect your vulnerability scanners, like Tenable or Qualys, to your AI platform. Automated integrations ensure scan results are enriched with relevant threat intelligence in real-time, while watch lists are updated as new threats emerge. This eliminates the need for manual data transfers and provides complete visibility into your environment, including shadow IT, containers, and cloud assets that could otherwise be overlooked.
With enriched feeds in place, you’re ready to move toward fully automated vulnerability monitoring.
Automating Vulnerability Monitoring and Updates
Once your threat intelligence is enriched, automation becomes the logical next step for maintaining continuous risk assessments.
Static vulnerability scores can quickly become outdated. A flaw that seems minor today might become a critical risk tomorrow if proof-of-concept exploit code is released or underground forums start discussing it. AI-driven scoring addresses this by dynamically updating risk levels based on real-time data.
Your AI system should automatically escalate a vulnerability’s priority when certain triggers occur – for instance, when exploit code is published, the vulnerability is mentioned on the dark web, it’s added to the CISA KEV catalog, or it’s linked to an active ransomware campaign. This dynamic recalibration happens without human intervention, keeping your risk assessments up-to-date.
Some advanced AI models can even predict Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) scores before vendors officially assign them. This capability allows your team to respond to zero-day threats faster. Considering that an exploit typically appears in the wild within 15 days of a vulnerability’s disclosure, this early warning could mean the difference between a smooth patching process and a full-blown emergency.
Integrating with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms takes this one step further. These platforms can reorder your patching priorities based on shifting risk levels. For example, if a vulnerability’s AI score spikes due to newly released exploit code, your SOAR system can automatically escalate the issue, notify the right team, and even initiate remediation workflows – all without manual input.
To keep pace with the rapidly evolving threat landscape, it’s crucial to retrain your AI algorithms regularly – ideally on a weekly basis. This ensures your risk assessments stay aligned with the latest attacker tactics and emerging vulnerabilities.
Setting Up AI-Powered Risk Scoring Models
Integrating AI into your vulnerability management process takes your patch prioritization to the next level. By layering intelligent analysis on top of automated monitoring and scanner data, AI helps refine how you address vulnerabilities.
The process begins with data ingestion and correlation. Your AI model needs to pull data from multiple sources – scanners, threat feeds like EPSS and CISA KEV, vendor advisories, and dark web monitoring. By correlating this data, the model builds a comprehensive view of each vulnerability’s threat level. Some models even use Large Language Models (LLMs) to translate technical advisories into straightforward remediation steps.
To handle the complexity of this data, many effective models rely on machine learning algorithms such as CatBoost. This algorithm is particularly adept at processing categorical data, like software names and vendor types, without requiring extensive manual preparation. Your AI system should focus on analyzing four key factors:
- Exploit likelihood (e.g., is weaponized code circulating?),
- Business impact (e.g., could sensitive data be exposed?),
- Environmental exposure (e.g., is the system internet-facing?),
- Control efficacy (e.g., are firewalls or other defenses reducing risk?).
A critical part of the setup is establishing continuous learning loops. AI models should be retrained regularly – ideally every week – using data from remediation outcomes, patch success rates, and new threat intelligence.
Deploying and Configuring AI Models
When rolling out your AI model, begin with a pilot program on low-risk or non-production systems before extending it to critical infrastructure. During this trial phase, configure the algorithm to assess specific technical factors, such as exploit code maturity, product coverage, and whether the vulnerability enables remote access or arbitrary code execution.
Using graph-based analysis to map relationships between vulnerabilities can improve prediction accuracy by up to 30%. Additionally, incorporate predictive analytics to estimate the operational impact of applying a patch – such as downtime, performance issues, or compatibility challenges. For instance, some implementations report a Mean Absolute Error of 0.63 in predicting CVSS scores when graph features are included.
Advanced AI models dynamically update risk scores daily for every CVE, factoring in new threat intelligence and dark web activity. This ensures that a vulnerability deemed low-risk yesterday could automatically escalate to critical if exploit code is detected online.
One of the biggest advantages of AI-driven risk scoring is its ability to drastically narrow down the vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention. For example, it can reduce the number of urgent vulnerabilities by 98.4%, identifying only the 1.6% that genuinely threaten your organization.
Once the initial deployment is complete, the next step is tailoring the AI model to align with your organization’s unique risk landscape.
Customizing Models for Your Organization
Customizing your AI model helps bridge the gap between technical risks and their business consequences, making your patch prioritization smarter and more aligned with your objectives. Start by creating an asset criticality map that classifies systems based on their business importance. For instance, a public-facing e-commerce portal managing payment data carries a far higher risk than an isolated test server, even if both share the same technical vulnerabilities.
Leverage CVSS Environmental metrics to adjust scores based on your infrastructure. For example, vulnerabilities in systems protected by strong network segmentation or firewalls can be rated lower. The AI should also account for compensating controls, such as intrusion prevention systems, which might effectively neutralize a high-severity vulnerability.
Integrating business service data into the AI model ensures that technical vulnerabilities are tied to business priorities. For example, a flaw in a primary revenue-generating server should take precedence over the same flaw in a noncritical internal tool. Add data classification tags like PCI, HIPAA, or GDPR to automatically prioritize vulnerabilities affecting regulated systems.
Define risk-tiered SLAs (e.g., Immediate, Rapid, Standard, Deferred) to align remediation timelines with the severity of the risk. For vulnerabilities that combine active exploitation with impacts on critical systems, assign a "Tier 0" status, requiring action within 24 hours.
| CVSS Metric Group | Customization Purpose |
|---|---|
| Base Metrics | Captures inherent characteristics (e.g., Attack Vector, Complexity, Privileges) |
| Temporal Metrics | Reflects real-world urgency (e.g., Exploit maturity, remediation level) |
| Environmental Metrics | Aligns risk with your infrastructure (e.g., Asset criticality, security requirements) |
Additionally, flag systems running end-of-life (EOL) software in your asset inventory. These systems should be prioritized regardless of AI scores since vendors no longer provide security updates. Use AI to map asset dependencies, highlighting how a vulnerability in one component (like a web application) could impact others (like a backend database).
Customizing your model requires collaboration beyond the IT and security teams. Work with executives and business leaders to define acceptable risk levels and downtime for different systems. As one Lead Technology Specialist at a Tech Business Services Firm explained:
"Asset management is not a problem until it becomes a problem. We once got hit with a six-figure Microsoft fine because we weren’t tracking what was actually deployed versus licensed. That made us realize that ‘critical’ means nothing without context."
Finally, ensure your AI platform provides explainable results. It should clearly document the reasoning behind each risk score, enabling you to justify prioritization decisions to stakeholders and auditors. This is especially important when patching a "Medium" CVSS vulnerability before a "Critical" one because the AI has identified active exploitation or business impact factors that CVSS alone cannot capture.
sbb-itb-9b7603c
Connecting AI Scoring with Patch Management Systems
Integrating AI scoring with patch management systems transforms the process of risk assessment into actionable solutions. Once you’ve tailored your AI model, the next step is to link it with your patch management setup. This connection enables you to turn theoretical risk scores into automated workflows, ensuring critical vulnerabilities are patched immediately while less urgent issues follow standard maintenance schedules.
This process often involves tying your AI scoring system to tools like Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) platforms and SIEM systems. For instance, you can use PowerShell scripts within your RMM tool to scan for AI-generated risk scores and assign priority tags to endpoints, such as "PatchPriority: Tier 1" or "PatchPriority: Tier 3", directly in the system registry. This tagging mechanism helps your patch management system identify which devices need urgent attention without manual intervention.
By integrating these systems, you create a shared framework for communication between security and IT teams. While security teams prioritize eliminating threats quickly, IT teams focus on maintaining system stability and minimizing downtime. As Karl Triebes, Chief Product Officer at Ivanti, puts it:
"Risk-based patch management… bridges the gap between security and IT teams by establishing shared priorities and a common language to address them".
Automating Patch Prioritization Workflows
Automation is where AI scoring truly shines. Start by creating a tiering model that organizes software based on its AI-assigned risk score. For example, Tier 1 might include software like Chrome or Microsoft Exchange on internet-facing servers, requiring patches within 24–48 hours. Tier 2 could cover systems like database servers, with a seven-day patching window. Tier 3 might apply to less critical software, such as HR systems, which can align with monthly vendor updates.
| Tier | Patch Window | Impacted Systems Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | 24–48 hours | Email servers, e-commerce platforms |
| Tier 2 | Within 7 days | Database servers, shared drives |
| Tier 3 | Monthly/Vendor | HR systems, digital signage, printers |
| Tier 4 | Access mitigation | Legacy systems requiring isolation |
The system should continuously refresh risk scores by pulling real-time threat intelligence from multiple sources. For example, if a vulnerability initially classified as low-risk becomes a target for ransomware or exploit kits, it can automatically escalate to Tier 1 status.
Integrating with SIEM systems further enhances this process. By correlating vulnerability data with active security events, such as intrusion attempts linked to specific CVEs, the AI scoring system can refine prioritization.
This level of automation significantly reduces workloads. Organizations that have shifted from CVSS-based prioritization to AI-powered Vulnerability Priority Ratings (VPR) report a 90% reduction in remediation efforts. While CVSS often flags 60% of vulnerabilities as "high" or "critical", AI-driven scoring narrows the focus to the 1.6% of vulnerabilities that pose genuine risks, cutting down unnecessary alerts by 98.4%.
Once the technical aspects of automation are in place, the next step is to align patching efforts with the organization’s broader business goals.
Aligning Patching with Business Priorities
AI scoring goes beyond technical risk – it helps prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on business operations. For example, a vulnerability on an internet-facing payment server that handles customer transactions should take precedence over the same vulnerability on an isolated test server, even if both have identical CVSS scores.
To achieve this alignment, integrate your AI model with asset inventories and business service data. Tag assets with metadata like "PCI-compliant", "revenue-generating", or "customer-facing" so the AI can weigh scores accordingly. This ensures that critical systems, like an e-commerce platform, are prioritized over less essential tools.
It’s also essential to consider operational constraints. AI scoring should account for factors like available maintenance windows, the risk of disrupting critical systems, and compensating controls such as firewalls or network segmentation. For instance, if a high-risk vulnerability affects a system protected by robust isolation measures and has no internet exposure, it might be scheduled for the next routine maintenance window instead of requiring an emergency patch.
AI scoring also simplifies compliance tracking. Roughly 35% of cybersecurity professionals report challenges in maintaining compliance with patching requirements, while 37% struggle with blind spots in patch configurations and SLA adherence. By automating patch prioritization, you can create detailed audit trails that demonstrate risk-based decision-making. These records can help satisfy regulatory requirements for frameworks like NIST CSF or ISO/IEC 27001, which demand documented risk management processes.
Measuring AI-Powered Patch Prioritization Results
Once you’ve integrated AI scoring into your patch management system, the next step is measuring its impact. Key metrics like Mean Time to Remediation (MTTR) and SLA compliance can help assess the effectiveness of AI-driven patch prioritization. For example, organizations using AI models report a 90% reduction in remediation workloads by focusing on the most critical vulnerabilities.
SLA compliance tracks how well you meet deadlines for addressing high-risk vulnerabilities, such as resolving "Tier 0" issues within 24 hours of detection. This is especially important given that, by 2024, the average time-to-exploit for new vulnerabilities dropped to less than a day.
Another critical metric is noise reduction, which measures how effectively your AI system filters out false positives. AI scoring narrows the focus to just 1.6% of vulnerabilities that pose genuine risks, compared to the 60% flagged as "high" or "critical" by traditional CVSS scores. You can also monitor your efficiency ratio, which reflects the percentage of vulnerabilities flagged by AI that attackers later attempt to exploit. A higher ratio indicates better precision.
Beyond technical data, tracking resource savings is equally important. Automated intelligence can save security teams an average of 15.9 hours per week on vulnerability investigations. Additionally, organizations using advanced vulnerability intelligence report an 86% reduction in unplanned downtime.
Key Performance Metrics to Track
A well-designed dashboard can help you monitor various dimensions of your patch management program. Here are some metrics to consider:
- Risk delta: Tracks the reduction in your organization’s overall risk score over time as prioritized patching takes effect.
- Exposure window: Measures the time between the public disclosure of a vulnerability and the implementation of a patch or mitigating control. This is especially relevant since 28% of vulnerabilities exploited in Q1 2025 had "Medium" CVSS base scores.
- Deferral rationale: For compliance purposes, document why certain "Critical" vulnerabilities were deprioritized, such as low exploit probability or existing compensating controls.
| Metric | Metric Focus | Success Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| MTTR | Speed of fixing critical flaws | Decrease in days/hours to remediate |
| SLA Compliance | Adherence to patch timelines | High percentage of Tier 0 patches resolved quickly |
| Efficiency Ratio | % of prioritized CVEs exploited | Higher ratio indicates better AI precision |
| Noise Reduction | Filtering out false alarms | Focus narrowed to 1.6% of vulnerabilities |
| Risk Delta | Change in overall risk score | Consistent downward trend |
These metrics provide a comprehensive view of both operational success and the broader impact of AI-powered patch prioritization.
Improving Risk Models Over Time
To keep up with evolving threats, AI models need regular updates. Incorporating incident data and control outcomes can refine prediction accuracy. For instance, if your endpoint detection system identifies an attempted exploitation, feeding that data back into your AI model can help adjust future scoring. This type of contextual enrichment ensures your model stays relevant.
Precision can also be evaluated using metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE). Adding graph-based features, such as analyzing the history of related vulnerabilities, can improve MAE by about 30%. Many organizations are now adopting composite scoring, which combines data from CVSS, EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System), and KEV (Known Exploited Vulnerabilities) for a more nuanced risk analysis.
One notable example comes from research conducted in October 2024. A relevance-based ranking model was tested on software used by six universities and four government facilities. By linking vulnerabilities to MITRE ATT&CK tactics through knowledge graphs, the model achieved a 71.5%–91.3% improvement in identifying exploited vulnerabilities and reduced annual remediation costs by 23.3%–25.5%. These results highlight how advanced AI models, when enriched with diverse data sources, can deliver measurable returns on investment.
However, AI scoring should complement, not replace, human expertise. As Chris Goettl, Vice President of Product Management at Ivanti, points out:
"Most of the vulnerabilities that are actively being targeted are not the ones that organizations are prioritizing, which is why we need a risk-based approach to patch prioritization and remediation".
Feedback from your security team is invaluable for refining AI models. If the system misses critical threats or over-prioritizes low-risk vulnerabilities, adjust its weighting factors accordingly. This human-in-the-loop approach ensures your AI scoring aligns with the actual challenges your organization faces.
Conclusion
AI-powered patch prioritization transforms the chaos of vulnerability data into a streamlined defense strategy. While traditional approaches often waste resources by spreading efforts too thin, AI scoring pinpoints the 1.6% of vulnerabilities that truly matter, reducing immediate remediation tasks by a staggering 98.4%.
By cutting remediation workloads by 90%, AI doesn’t just save time – it fosters collaboration between security and IT teams. It creates a shared framework for prioritizing and addressing threats, bridging gaps that often slow down response efforts. This level of efficiency sets the stage for automated systems to manage vulnerability data with unmatched accuracy.
Automation plays a key role here. Tools like The Security Bulldog use natural language processing (NLP) to process vast amounts of information, including CVEs, MITRE ATT&CK data, and threat intelligence feeds. This reduces manual research time by about 80%, allowing security teams to focus on tackling high-impact threats instead of drowning in data.
As these efficiencies take root, the importance of moving from reactive to proactive patching becomes clear. With vulnerability exploitation surging by 180% year-over-year and contributing to 14% of all data breaches, relying solely on static CVSS scores is no longer sufficient. AI scoring evolves in real time, factoring in active exploit trends, business priorities, and asset importance to ensure that only the most critical vulnerabilities are addressed immediately.
FAQs
How does AI scoring help prioritize vulnerabilities more effectively than CVSS?
AI scoring takes vulnerability assessment to the next level by integrating real-time data – including exploit activity, asset exposure, and contextual threat intelligence. This creates a dynamic risk rating that adapts to the current environment, highlighting vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited and posing the greatest risk to your specific setup.
On the other hand, CVSS scores remain static, relying only on generic technical severity. This limitation means they might not account for the constantly changing threat landscape. With AI-driven insights, you can pinpoint and address the most pressing vulnerabilities more efficiently, helping to lower your organization’s overall risk.
How can I integrate AI scoring into my security processes?
To bring AI scoring into your security processes, start by outlining its scope. Pinpoint the assets, vulnerability feeds, and patching cycles you want to evaluate. Define clear objectives – whether it’s cutting down risk exposure or trimming remediation costs. Once that’s set, gather all necessary data – like vulnerability scans, asset inventories, threat intelligence, and business context – and store it in one centralized location. This gives the AI platform a comprehensive view of your environment.
From there, the AI platform steps in, using methods like natural language processing and predictive analytics to generate risk-based scores. These scores don’t just look at technical severity; they also consider the business impact, making it easier to prioritize patches. Even better, these scores can integrate directly with your ticketing or patch management systems, smoothing out the planning and execution of remediation tasks.
The process doesn’t stop there – it’s designed to evolve. Feedback from completed remediation efforts is fed back into the AI system, improving its accuracy and effectiveness over time. Platforms such as The Security Bulldog make this integration easier, offering built-in tools that cut down manual work while boosting decision-making efficiency. This approach not only saves your team time but also optimizes your resources.
How can AI scoring help reduce the effort and downtime involved in patching?
AI scoring simplifies patch management by evaluating vulnerabilities through real-time exploit probability and potential impact on the business. This approach helps teams concentrate on tackling the most pressing risks first, cutting down the overall number of patches needed.
By focusing on high-risk vulnerabilities, companies can reduce system downtime, allocate resources more effectively, and maintain a secure environment with fewer interruptions.